Hudson river map 13 colonies – Embark on a historical journey through the Hudson River Valley, where the destiny of the 13 colonies was shaped by the river’s majestic flow. From its strategic location to its cultural heritage, the Hudson River played a pivotal role in the development of the United States.
This comprehensive guide will navigate you through the river’s geography, historical events, economic significance, and cultural legacy, offering a captivating exploration of its enduring impact on American history.
Historical Context
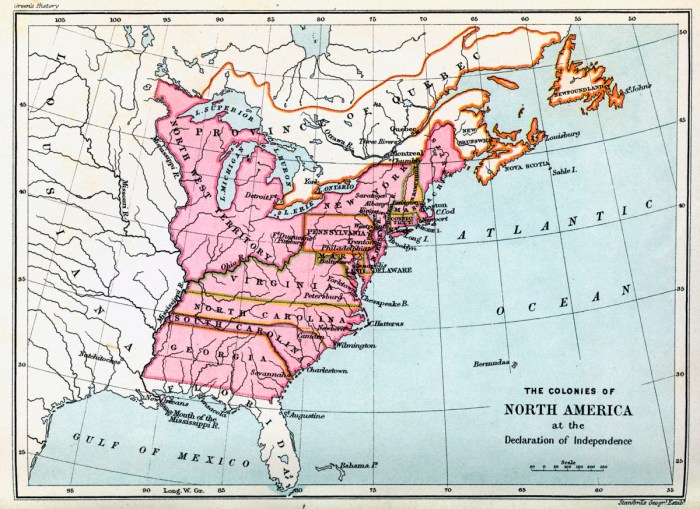
The Hudson River played a pivotal role in the development of the 13 colonies. As a major waterway connecting the Atlantic Ocean to the interior of the continent, it provided a vital means of transportation, trade, and settlement.
From the early days of European exploration, the Hudson River served as a gateway to the interior of North America. Dutch settlers established the colony of New Netherland along the river’s banks in the 17th century, and the English later took control of the area in the 17th century.
Trade and Transportation
The Hudson River facilitated the growth of trade and commerce between the colonies and Europe. The river provided a convenient route for the transportation of goods such as furs, timber, and agricultural products to and from markets in Europe and the Caribbean.
The river also played a crucial role in the development of the fur trade. Dutch and English traders established trading posts along the river’s banks, where they exchanged European goods for beaver pelts and other valuable furs.
Settlement
The Hudson River Valley was a major destination for European settlers in the 18th century. The fertile land along the river’s banks attracted farmers, and the river provided a convenient means of transportation for settlers to reach the interior of the continent.
The growth of settlements along the Hudson River led to the development of towns and cities, such as New York City, Albany, and Poughkeepsie. These urban centers became important centers of commerce and culture in the colonies.
Geographic Features
The Hudson River, a majestic waterway that played a pivotal role in the development of the United States, boasts a unique course and a plethora of captivating geographic features along its banks.
Originating in the Adirondack Mountains of upstate New York, the Hudson River flows south for approximately 315 miles before emptying into the Atlantic Ocean at New York Harbor. Along its journey, the river carves a picturesque valley through the rugged Appalachian Mountains, creating a dramatic backdrop for the vibrant cities and towns that line its shores.
Major Tributaries
The Hudson River is fed by several major tributaries, each contributing to its impressive flow. The Mohawk River, the largest tributary, joins the Hudson at the city of Troy, New York. Other significant tributaries include the Schoharie Creek, the Esopus Creek, and the Rondout Creek.
Key Geographic Features
- The Palisades: A series of steep cliffs that rise along the west bank of the river in New Jersey, offering breathtaking views of the Hudson Valley.
- Storm King Mountain: A prominent peak located on the east bank of the river in New York, known for its rugged beauty and challenging hiking trails.
- West Point: A historic military academy situated on a strategic point overlooking the Hudson River, where the river makes a sharp bend.
- The Tappan Zee Bridge: A major bridge that spans the Hudson River between Tarrytown, New York, and South Nyack, New York, providing a vital transportation link between the two sides of the river.
- Ellis Island: A former immigration station located in New York Harbor, where millions of immigrants entered the United States between 1892 and 1954.
Map Analysis
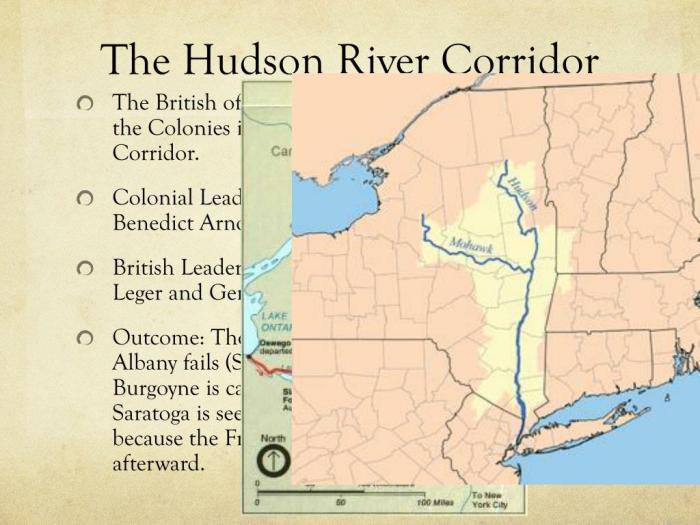
The Hudson River, flowing through the heart of the 13 colonies, played a pivotal role in shaping their history and development. By analyzing the map, we can gain insights into the strategic importance of the river and identify key landmarks that influenced the course of events.
Major cities and towns along the river include New York City, Albany, Troy, and Poughkeepsie. The river also boasts significant landmarks such as West Point, the site of a crucial military academy, and the Palisades, a stunning natural rock formation.
Strategic Importance
The Hudson River’s strategic location made it a vital transportation route, connecting the Atlantic Ocean to the interior of the colonies. It allowed for the movement of goods, people, and ideas, facilitating trade and communication. Moreover, the river’s defensible position, with high ground on either side, made it a strategic military asset, particularly during the Revolutionary War.
Historical Events
The Hudson River served as a pivotal stage for numerous historical events that shaped the development of the 13 colonies. These events ranged from battles and treaties to explorations and settlements, leaving an enduring impact on the region’s history and legacy.
One of the most significant events was the exploration of the river by Henry Hudson in 1609. Hudson’s voyage opened up the waterway to European colonization and trade, paving the way for the establishment of the Dutch colony of New Netherland.
Albany Congress, Hudson river map 13 colonies
In 1754, the Albany Congress convened in Albany, New York, with the aim of fostering unity and cooperation among the British colonies in North America. The congress, attended by delegates from seven colonies, discussed issues related to defense and relations with Native American tribes.
The Hudson River played a pivotal role in the development of the Thirteen Colonies. Its navigable waters provided a vital transportation route for trade and settlement. While exploring the Hudson River map, one might stumble upon an intriguing question: what is the ideal golf stance width in inches? Discover the answer to this and more by clicking here . Returning to our exploration of the Hudson River map, it’s fascinating to note the strategic locations of settlements along its banks, shaping the destiny of the Thirteen Colonies.
Despite its efforts, the Albany Congress failed to achieve its primary objectives due to disagreements among the colonies.
Battles of Saratoga
During the American Revolutionary War, the Hudson River Valley witnessed two pivotal battles: the Battles of Saratoga in 1777. These battles, fought near the town of Saratoga, resulted in decisive victories for the Continental Army under General Horatio Gates. The victories at Saratoga boosted the morale of the American forces and convinced France to enter the war on their side, turning the tide of the conflict in favor of the Americans.
The Erie Canal
In the early 19th century, the construction of the Erie Canal along the Hudson River marked a major milestone in American transportation and economic development. The canal connected the Great Lakes to the Atlantic Ocean, facilitating the flow of goods and people between the East and the West.
The Erie Canal played a crucial role in the growth of New York City as a major commercial hub and contributed to the expansion of the United States.
Economic Significance: Hudson River Map 13 Colonies
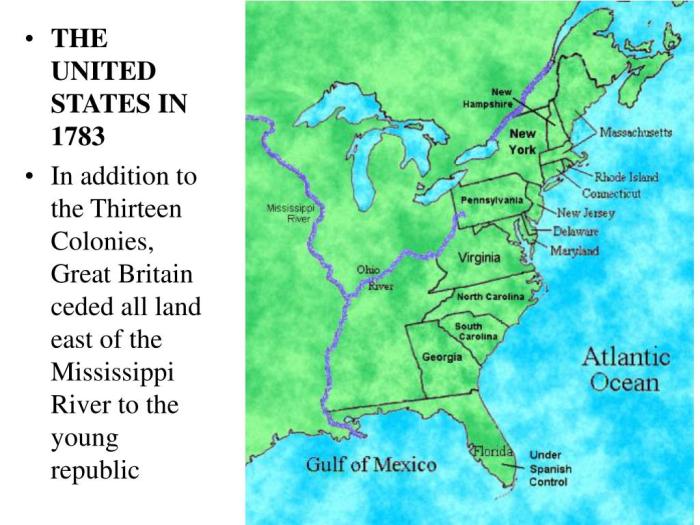
The Hudson River played a pivotal role in the economic prosperity of the 13 colonies. Its navigable waters and fertile lands fostered the growth of various industries and facilitated trade and commerce.
Along the riverbanks, settlements and towns flourished, engaging in diverse economic activities.
Industries and Resources
- Agriculture:The fertile Hudson Valley provided abundant farmland for growing crops such as wheat, corn, and vegetables. Farmers supplied produce to local markets and exported surplus to other colonies and beyond.
- Fishing:The river’s teeming waters supported a thriving fishing industry. Fishermen caught a variety of species, including sturgeon, shad, and oysters, which were sold for food and profit.
- Fur Trade:The Hudson River served as a major trade route for the fur trade. Native American trappers brought beaver pelts to trading posts along the river, which were then shipped to Europe for lucrative profits.
- Timber:The forests surrounding the river provided a vast supply of timber. Lumberjacks harvested trees for construction, shipbuilding, and other industries.
- Mining:The Hudson Valley was rich in mineral resources, including iron ore and limestone. Mining operations supplied raw materials for industries and construction projects.
Trade and Commerce
The Hudson River’s navigable waters made it an essential transportation route for goods and people. Ships and boats carried agricultural products, manufactured goods, and raw materials between settlements and colonies.
The river also facilitated trade with Native American tribes. European colonists exchanged European goods for furs, food, and other resources.
Cultural Heritage
The Hudson River holds immense cultural significance, inspiring countless artistic, literary, and musical creations.The river’s scenic beauty and historic importance have captivated writers, painters, and musicians for centuries. The Hudson River School, a group of 19th-century American landscape painters, found inspiration in the river’s picturesque vistas.
Their works, such as Thomas Cole’s “View from Mount Holyoke, Northampton, Massachusetts, after a Thunderstorm—The Oxbow” (1836), depicted the river’s grandeur and the surrounding natural landscape.
Literary Works
The Hudson River has also featured prominently in American literature. Washington Irving’s “The Legend of Sleepy Hollow” (1820) immortalized the river’s mysterious atmosphere, while Herman Melville’s “Moby-Dick” (1851) used the river as a symbol of the unknown and the sublime.
Musical Works
The river’s musical heritage is equally rich. The Hudson River Valley has been a center for folk music, with songs like “The Hudson River Song” (1867) and “Shenandoah” (1882) celebrating the river’s beauty and importance.
Cultural Landmarks and Traditions
Along the Hudson River, numerous cultural landmarks and traditions connect the past to the present. The Palisades, a series of steep cliffs along the west bank, have been a popular tourist destination since the 19th century. The Hudson River Valley National Heritage Area, established in 1996, preserves the river’s cultural and natural resources.The
river also plays a vital role in annual events such as the Hudson River Maritime Festival and the Hudson Valley Garlic Festival. These festivals showcase the region’s cultural heritage and promote the river’s importance as a source of recreation and community.
Essential Questionnaire
What was the strategic importance of the Hudson River?
The Hudson River provided a vital transportation route for goods and people, connecting the Atlantic Ocean to the interior of the continent. It also served as a defensive barrier, protecting the colonies from attacks by European powers.
How did the Hudson River contribute to the economic development of the 13 colonies?
The river supported a thriving trade in agricultural products, furs, and other goods. It also facilitated the growth of industries such as shipbuilding, fishing, and milling.
What are some of the major historical events that occurred along the Hudson River?
The river witnessed numerous pivotal events, including the founding of New York City, the American Revolution, and the westward expansion of the United States.