Dive into the world of medical coding with CPT code for triple arthrodesis. This comprehensive guide will explore the ins and outs of this surgical procedure, its indications, contraindications, and more, in a captivating and informative way.
Triple arthrodesis is a surgical procedure that involves fusing three joints in the foot to correct severe deformities or arthritis. Understanding the CPT code associated with this procedure is crucial for accurate billing and insurance purposes.
CPT Code Definition
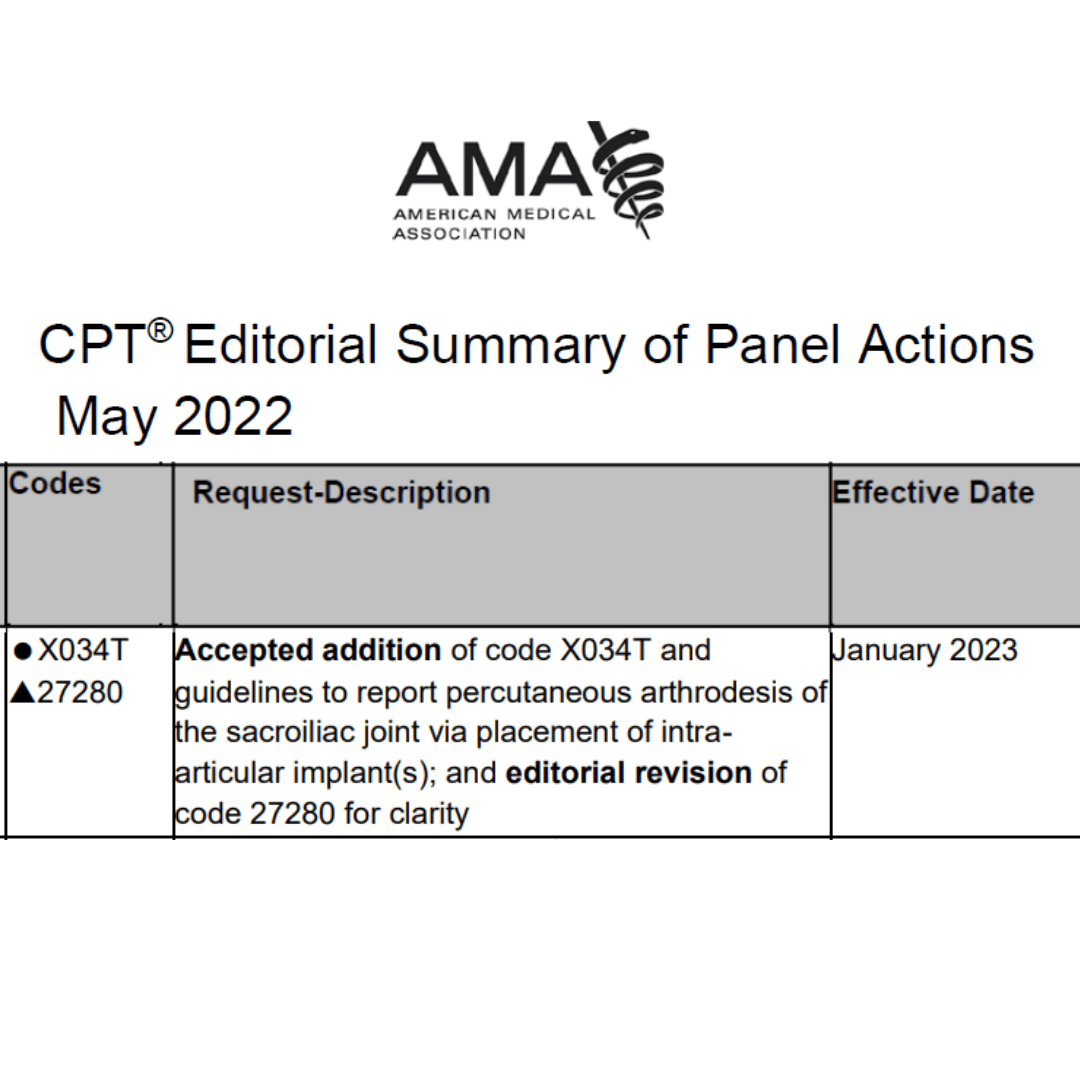
Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) codes are a standardized set of medical codes used to describe and report procedures, services, and supplies provided by healthcare professionals to patients.
The CPT code for triple arthrodesis is 28330.
Purpose of CPT Codes, Cpt code for triple arthrodesis
CPT codes serve several essential purposes within the medical industry:
- Accurate Billing:CPT codes enable healthcare providers to accurately bill insurance companies and patients for services rendered.
- Uniformity:They provide a standardized language for describing medical procedures, ensuring consistent communication and documentation among healthcare professionals.
- Data Collection:CPT codes facilitate the collection and analysis of data related to healthcare utilization, costs, and outcomes.
- Quality Assurance:By tracking the procedures performed, CPT codes can assist in monitoring the quality of care provided by healthcare providers.
Triple Arthrodesis Procedure
Triple arthrodesis is a surgical procedure that involves fusing three joints in the foot: the talonavicular joint, the calcaneocuboid joint, and the subtalar joint. This procedure is typically performed to treat severe arthritis or deformity of the foot.
Surgical Procedure
The surgical procedure for triple arthrodesis typically involves the following steps:
- The surgeon makes an incision on the top of the foot.
- The surgeon removes the cartilage from the surfaces of the three joints.
- The surgeon prepares the bones by shaping them and removing any spurs or deformities.
- The surgeon aligns the bones and fixes them together with screws, plates, or rods.
- The surgeon closes the incision and applies a cast or splint to the foot.
Post-Operative Care and Recovery
After surgery, the patient will typically stay in the hospital for 2-3 days. During this time, the patient will be given pain medication and antibiotics. The patient will also be instructed on how to care for the foot and how to use crutches or a walker.The
patient will need to keep the foot elevated and avoid putting weight on it for 6-8 weeks. During this time, the patient will need to use crutches or a walker to get around. The patient will also need to see the surgeon regularly for follow-up appointments to monitor the healing process.Most
patients can expect to return to normal activities within 3-6 months after surgery. However, it may take up to a year for the foot to fully heal.
Indications and Contraindications
Triple arthrodesis is a surgical procedure that involves fusing the three joints of the hindfoot: the subtalar, talonavicular, and calcaneocuboid joints. This procedure is typically performed to correct severe deformities of the foot and ankle, such as flatfoot, clubfoot, or arthritis.
There are several common indications for triple arthrodesis, including:
- Severe flatfoot deformity
- Clubfoot deformity
- Arthritis of the hindfoot joints
- Fractures or dislocations of the hindfoot joints
- Failed previous surgeries on the hindfoot
As with any surgical procedure, there are potential risks and complications associated with triple arthrodesis. These include:
- Infection
- Bleeding
- Nerve damage
- Delayed wound healing
- Stiffness of the hindfoot
- Failure of the fusion
There are also certain contraindications that may prevent a patient from undergoing triple arthrodesis. These include:
- Active infection
- Poor circulation to the foot
- Severe neuropathy
- Uncontrolled diabetes
- Obesity
Patient Selection and Evaluation
Patient selection is crucial for successful triple arthrodesis outcomes. Suitable candidates are typically individuals with severe ankle and hindfoot deformities, pain, and functional limitations. Factors considered include the patient’s age, medical history, activity level, and the severity of the deformity.
Pre-operative Evaluation
Pre-operative evaluation involves a thorough physical examination to assess the range of motion, alignment, and stability of the ankle and hindfoot. Imaging studies, such as X-rays and MRI scans, are essential to visualize the extent of the deformity and identify any underlying pathology.
A comprehensive medical history review is conducted to identify any conditions that may affect the surgery or recovery, such as diabetes, vascular disease, or previous infections.
Patient Education and Informed Consent
Patient education and informed consent are vital before surgery. Patients should be thoroughly informed about the procedure, potential risks and benefits, alternative treatment options, and the expected recovery timeline. They should have the opportunity to ask questions and clarify any concerns to make an informed decision about the surgery.
Surgical Techniques
Triple arthrodesis can be performed using various surgical techniques, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The choice of technique depends on the surgeon’s preference, the patient’s anatomy, and the extent of the deformity.
Open Technique
The open technique is the most common approach to triple arthrodesis. It involves making an incision over the affected joints and directly visualizing the bones and ligaments. This technique allows for precise placement of the implants and thorough debridement of the arthritic surfaces.
Advantages:
- Precise implant placement
- Thorough debridement
- Suitable for complex deformities
Disadvantages:
- Larger incision
- Longer recovery time
- Higher risk of infection
Percutaneous Technique
The percutaneous technique is a minimally invasive approach that involves making small incisions and using fluoroscopic guidance to place the implants. This technique minimizes soft tissue damage and reduces the risk of infection.
Advantages:
- Smaller incisions
- Less soft tissue damage
- Lower risk of infection
Disadvantages:
- Less precise implant placement
- Not suitable for complex deformities
- Longer learning curve for surgeons
Combined Technique
The combined technique combines the open and percutaneous approaches. It involves making a small incision for fluoroscopic guidance and then using open techniques to complete the arthrodesis.
Advantages:
- Combines the advantages of both open and percutaneous techniques
- Suitable for a wider range of deformities
- Reduces the risk of infection compared to open technique
Disadvantages:
The CPT code for triple arthrodesis, a surgical procedure to fuse three bones in the foot, is a topic that can be further explored in the context of vocabulary expansion. To enhance your understanding of medical terminology related to the foot and ankle, consider exploring vocab workshop level e unit 2 . This resource provides a comprehensive overview of relevant terms, helping you to grasp the intricacies of triple arthrodesis and other foot-related procedures.
- Larger incision than percutaneous technique
- Longer recovery time than percutaneous technique
- Higher risk of infection than percutaneous technique
Outcomes and Complications

Triple arthrodesis aims to alleviate pain, enhance foot function, and improve overall quality of life for individuals with severe ankle and hindfoot deformities. The procedure involves fusing three joints in the hindfoot: the talonavicular, calcaneocuboid, and subtalar joints.
Post-operatively, patients typically experience significant pain relief and improved mobility. The fusion of the hindfoot joints stabilizes the foot and corrects deformities, enabling patients to walk more comfortably and engage in activities that were previously challenging.
Potential Complications
As with any surgical procedure, triple arthrodesis carries potential complications. These include:
- Infection:Bacterial infections can occur at the surgical site, requiring antibiotics or further surgical intervention.
- Non-union:Failure of the bones to fuse properly, leading to persistent pain and instability.
- Hardware failure:Screws or plates used to stabilize the fused joints may loosen or break, requiring revision surgery.
The management of complications involves addressing the underlying cause and providing appropriate treatment. This may include antibiotics for infections, additional surgery for non-union, or hardware revision in cases of hardware failure.
Rehabilitation and Recovery: Cpt Code For Triple Arthrodesis
Following triple arthrodesis, patients undergo a rehabilitation program to restore mobility and function to the affected foot and ankle. This program typically involves a combination of physical therapy, weight-bearing restrictions, and activity modifications.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in the rehabilitation process. It helps patients regain range of motion, strength, and stability in the foot and ankle. Physical therapists may use various techniques, including:
- Exercises to improve flexibility and range of motion
- Strengthening exercises to build muscle strength
- Balance exercises to improve stability
- Gait training to relearn how to walk properly
Weight-Bearing Restrictions
After surgery, patients are typically restricted from bearing weight on the affected foot for a period of time. This helps to protect the healing bones and joints. Weight-bearing restrictions may be gradually increased as the foot heals.
Activity Modifications
Patients may need to modify their activities during the recovery period. This may include avoiding high-impact activities, such as running or jumping. Patients may also need to use assistive devices, such as crutches or a walker, for a period of time.
Expected Recovery Timeline
The recovery timeline for triple arthrodesis varies from patient to patient. However, most patients can expect to experience the following milestones:
- 0-6 weeks:Non-weight-bearing on the affected foot, with physical therapy focusing on range of motion and pain management.
- 6-12 weeks:Gradual weight-bearing is allowed, with continued physical therapy to improve strength and stability.
- 3-6 months:Most patients are able to walk without assistive devices and resume most activities.
- 6-12 months:Full recovery and return to all activities, including sports.
Factors that may influence the recovery timeline include the severity of the arthritis, the patient’s overall health, and their compliance with the rehabilitation program.
Query Resolution
What is the purpose of CPT codes?
CPT codes are used to standardize the reporting of medical procedures and services for billing purposes, ensuring accurate and consistent documentation.
What are the indications for triple arthrodesis?
Triple arthrodesis is typically performed to correct severe deformities or arthritis in the foot, such as flatfoot, clubfoot, or Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease.
What are the potential complications of triple arthrodesis?
Potential complications include infection, non-union of the bones, hardware failure, and nerve damage.