Beginning with the benzoin to benzil balanced equation, this comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of this fundamental chemical transformation, exploring its significance, applications, and underlying mechanisms.
Benzoin, a fascinating organic compound, undergoes a remarkable conversion to benzil, a versatile intermediate in various chemical processes. The balanced equation for this reaction serves as a cornerstone for understanding the stoichiometry and energetics of this transformation.
Benzoin Structure and Properties
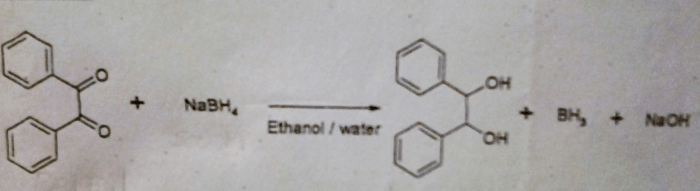
Benzoin is an organic compound with the molecular formula C 14H 12O 2. It is a white or pale yellow solid with a sweet, vanilla-like odor. Benzoin is insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents such as alcohol, ether, and chloroform.Benzoin
has a molecular structure consisting of two benzene rings connected by a carbonyl group. The two benzene rings are in a trans configuration, meaning that the hydrogen atoms on the two rings are on opposite sides of the molecule. The carbonyl group is located between the two benzene rings and is flanked by two hydroxyl groups.
Physical Properties, Benzoin to benzil balanced equation
Benzoin is a white or pale yellow solid with a melting point of 134-136 °C and a boiling point of 344 °C. It is insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents such as alcohol, ether, and chloroform.
Chemical Properties
Benzoin is a reactive compound that can undergo a variety of chemical reactions. It is easily oxidized to form benzil, and it can also be reduced to form hydrobenzoin. Benzoin can also undergo a variety of other reactions, including dehydration, condensation, and addition reactions.
Benzil Structure and Properties: Benzoin To Benzil Balanced Equation
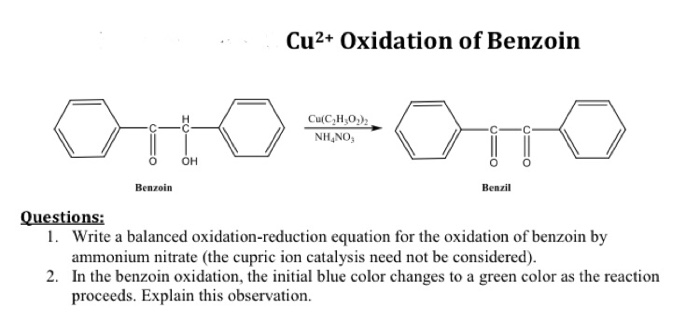
Benzil is an organic compound with the molecular formula C 14H 10O 2. It is a white or pale yellow solid with a melting point of 95-97 °C and a boiling point of 290-292 °C. Benzil is insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents such as alcohol, ether, and chloroform.Benzil
has a molecular structure consisting of two benzene rings connected by a carbonyl group. The two benzene rings are in a cis configuration, meaning that the hydrogen atoms on the two rings are on the same side of the molecule.
The carbonyl group is located between the two benzene rings and is flanked by two hydrogen atoms.
Physical Properties, Benzoin to benzil balanced equation
Benzil is a white or pale yellow solid with a melting point of 95-97 °C and a boiling point of 290-292 °C. It is insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents such as alcohol, ether, and chloroform.
Chemical Properties
Benzil is a reactive compound that can undergo a variety of chemical reactions. It is easily reduced to form benzoin, and it can also undergo a variety of other reactions, including dehydration, condensation, and addition reactions.
Common Queries
What is the significance of the benzoin to benzil balanced equation?
The balanced equation provides a quantitative understanding of the stoichiometry and energetics of the reaction, enabling chemists to optimize reaction conditions and predict product yields.
What are the applications of benzil?
Benzil finds applications in organic synthesis, medicinal chemistry, and as an intermediate in the production of dyes and pharmaceuticals.