Delve into the captivating realm of seismology with our comprehensive “Finding Epicenters Lab Answer Key.” This guide unlocks the secrets of earthquake analysis, empowering you to unravel the mysteries beneath the Earth’s surface.
As we embark on this scientific journey, we will explore the fundamentals of seismic waves, the art of triangulation, and the meticulous steps involved in determining the epicenter of an earthquake. Our interactive lab procedure, complete with a detailed experimental setup, will provide hands-on experience in unraveling earthquake data.
Seismic Waves
Seismic waves are vibrations that travel through the Earth’s materials. They are caused by sudden releases of energy, such as earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and explosions. Seismic waves can be used to study the Earth’s interior and to locate the epicenters of earthquakes.
There are three main types of seismic waves: P-waves, S-waves, and surface waves. P-waves are the fastest type of seismic wave and can travel through both solids and liquids. S-waves are slower than P-waves and can only travel through solids.
Surface waves are the slowest type of seismic wave and travel along the Earth’s surface.
Seismic waves are used to locate the epicenters of earthquakes by using a technique called triangulation. Triangulation is a method of determining the location of a point by measuring the angles between it and two known points. In the case of earthquakes, the known points are seismic stations that record the arrival times of the seismic waves.
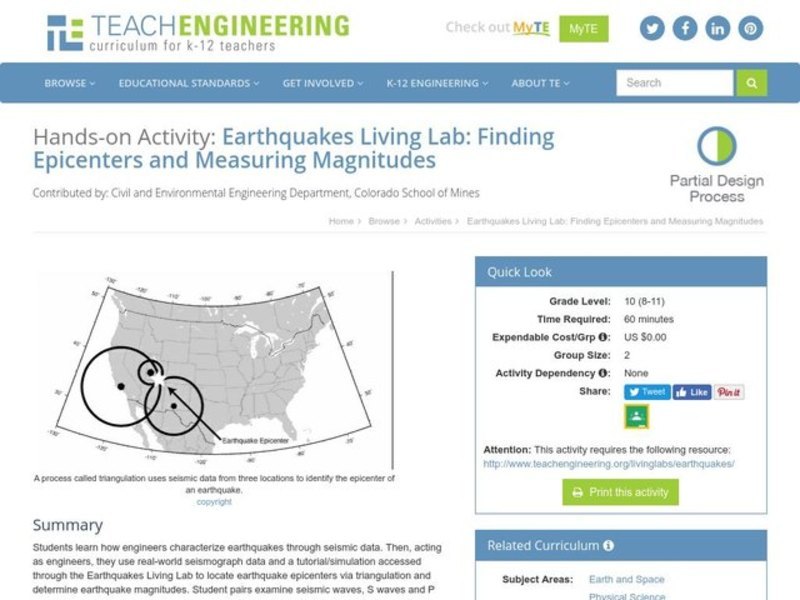
Triangulation
Triangulation is a method of determining the location of a point by measuring the angles between it and two known points. In the case of earthquakes, the known points are seismic stations that record the arrival times of the seismic waves.
To use triangulation to locate the epicenter of an earthquake, the following steps are taken:
- The arrival times of the seismic waves at each seismic station are recorded.
- The distances between the seismic stations and the epicenter are calculated.
- The angles between the lines connecting the seismic stations and the epicenter are calculated.
- The epicenter is located at the point where the three lines intersect.
Triangulation is a powerful tool for locating the epicenters of earthquakes. It is accurate and can be used to locate epicenters anywhere in the world.
Triangulation is also used in other fields, such as surveying, navigation, and astronomy.
Epicenter Determination

The epicenter of an earthquake is the point on the Earth’s surface directly above the hypocenter, the point where the earthquake occurs. The epicenter is important because it is the point where the most damage is likely to occur.
To determine the epicenter of an earthquake, the following steps are taken:
- The arrival times of the seismic waves at each seismic station are recorded.
- The distances between the seismic stations and the epicenter are calculated.
- The angles between the lines connecting the seismic stations and the epicenter are calculated.
- The epicenter is located at the point where the three lines intersect.
The accuracy of epicenter determination depends on the number of seismic stations that are used and the quality of the data. The more seismic stations that are used, the more accurate the epicenter determination will be.
Factors that can affect the accuracy of epicenter determination:, Finding epicenters lab answer key
- The number of seismic stations that are used.
- The quality of the data.
- The distance between the seismic stations and the epicenter.
- The complexity of the Earth’s crust.
Query Resolution: Finding Epicenters Lab Answer Key
What are the different types of seismic waves?
Seismic waves are categorized into body waves (P-waves and S-waves) and surface waves (Love waves and Rayleigh waves), each with distinct characteristics and propagation patterns.
How does triangulation aid in finding epicenters?
Triangulation utilizes the time difference between seismic wave arrivals at multiple stations to form triangles, allowing scientists to pinpoint the earthquake’s epicenter.
What factors can affect the accuracy of epicenter determination?
Factors such as the distribution and accuracy of seismic stations, the complexity of the Earth’s structure, and the signal-to-noise ratio of the seismic data can influence the precision of epicenter determination.