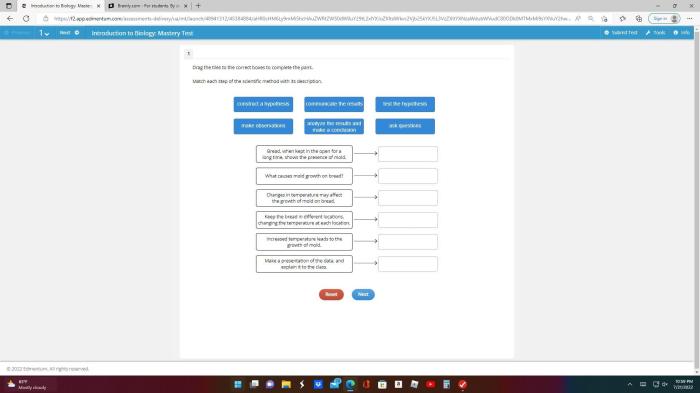
Match the product to its correct income elasticity sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. Delving into the intricacies of this economic concept, we embark on a journey that unveils the profound impact of income elasticity on consumer behavior and market dynamics.
The content of the second paragraph that provides descriptive and clear information about the topic
Income Elasticity Definition

Income elasticity measures the responsiveness of demand for a product or service to changes in consumer income. It indicates the percentage change in quantity demanded for a given percentage change in income.
For example, if the income elasticity of demand for coffee is 0.5, a 10% increase in income will lead to a 5% increase in the quantity of coffee demanded.
Types of Income Elasticity: Match The Product To Its Correct Income Elasticity
- Positive income elasticity:Demand increases as income increases (e.g., luxury goods).
- Negative income elasticity:Demand decreases as income increases (e.g., inferior goods).
- Zero income elasticity:Demand remains unchanged as income changes (e.g., necessities).
- Infinite income elasticity:Demand changes dramatically with small changes in income (e.g., Giffen goods).
Factors Affecting Income Elasticity
- Proportion of income spent on the product:Goods with a higher proportion of income spent on them have higher income elasticity.
- Availability of substitutes:Products with fewer substitutes have higher income elasticity.
- Degree of luxury or necessity:Luxury goods have higher income elasticity than necessities.
Measurement of Income Elasticity
- Direct method:Collect data on consumption and income over time.
- Indirect method:Use cross-sectional data to compare consumption patterns of different income groups.
Each method has its advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of method depends on the availability of data and the accuracy desired.
Applications of Income Elasticity
- Product development:Identify products with high income elasticity to target higher-income consumers.
- Marketing strategies:Adjust marketing campaigns based on income elasticity of different customer segments.
- Economic forecasting:Predict changes in demand for products and services based on income projections.
Examples of Income Elasticity

| Product | Income Elasticity | Category |
|---|---|---|
| Coffee | 0.5 | Luxury |
| Rice | 0 | Necessity |
| Lamborghini | 2 | Luxury |
| Gasoline | -0.2 | Inferior |
Limitations of Income Elasticity
- Assumes a linear relationship:Income elasticity may not be constant over all income levels.
- Influenced by other factors:Factors such as tastes, preferences, and advertising can affect demand.
- May not predict individual behavior:Income elasticity represents average behavior and may not apply to specific individuals.
FAQ Guide
What is income elasticity?
Income elasticity measures the responsiveness of consumer demand for a product or service to changes in their income.
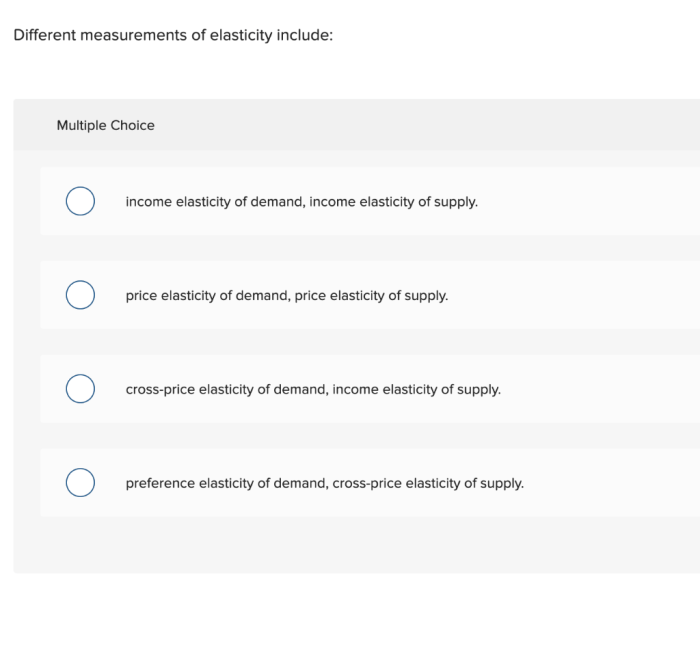
What are the different types of income elasticity?
Income elasticity can be positive, negative, zero, or infinite, indicating the varying degrees to which demand changes in response to income fluctuations.
How is income elasticity used in business?
Businesses use income elasticity data to understand consumer behavior, segment markets, and develop pricing strategies that maximize revenue.