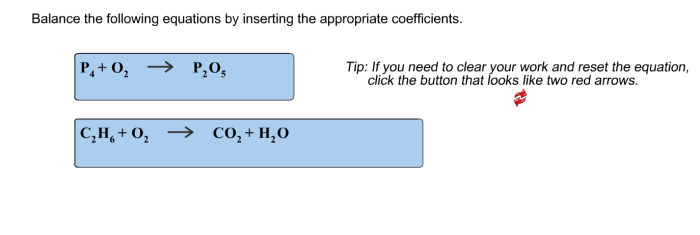
Balance the given equations by inserting the appropriate coefficients – Balancing given equations by inserting appropriate coefficients is a crucial aspect of chemistry that enables us to comprehend and predict chemical reactions accurately. This comprehensive guide delves into the concept of balancing equations, exploring methods and providing step-by-step instructions to achieve balanced chemical equations.
Understanding the principles of balancing equations empowers chemists to analyze and interpret chemical reactions, ensuring stoichiometrically correct proportions of reactants and products. This knowledge is essential for various applications, including chemical synthesis, industrial processes, and environmental chemistry.
Balancing Equations: Balance The Given Equations By Inserting The Appropriate Coefficients

In chemistry, a balanced equation is a chemical equation in which the number of atoms of each element on the reactants’ side of the equation is equal to the number of atoms of that element on the products’ side of the equation.
Unbalanced equations are chemical equations in which the number of atoms of each element on the reactants’ side of the equation is not equal to the number of atoms of that element on the products’ side of the equation.
Balancing equations is important because it allows us to determine the stoichiometry of a reaction, which is the quantitative relationship between the reactants and products of a reaction.
Methods for Balancing Equations
There are two main methods for balancing equations: the oxidation-reduction method and the half-reaction method.
Oxidation-Reduction Method
The oxidation-reduction method is based on the principle that in any chemical reaction, the total number of electrons lost by the reactants is equal to the total number of electrons gained by the products.
To balance an equation using the oxidation-reduction method, we first need to identify the oxidation and reduction half-reactions. The oxidation half-reaction is the reaction in which a substance loses electrons, and the reduction half-reaction is the reaction in which a substance gains electrons.
Once we have identified the oxidation and reduction half-reactions, we can balance them by adding electrons to the oxidation half-reaction and removing electrons from the reduction half-reaction. We can then add the two half-reactions together to get the balanced equation.
Half-Reaction Method
The half-reaction method is based on the principle that in any chemical reaction, the total number of atoms of each element on the reactants’ side of the equation is equal to the total number of atoms of that element on the products’ side of the equation.
To balance an equation using the half-reaction method, we first need to divide the equation into two half-reactions, one for the oxidation and one for the reduction.
We can then balance each half-reaction by adding atoms and electrons to the reactants and products until the number of atoms of each element and the number of electrons are equal on both sides of the half-reaction.
Once we have balanced the half-reactions, we can add them together to get the balanced equation.
Steps for Balancing Equations
Steps for Balancing Equations Using the Oxidation-Reduction Method
- Identify the oxidation and reduction half-reactions.
- Balance the oxidation and reduction half-reactions by adding electrons to the oxidation half-reaction and removing electrons from the reduction half-reaction.
- Add the two half-reactions together to get the balanced equation.
Steps for Balancing Equations Using the Half-Reaction Method
- Divide the equation into two half-reactions, one for the oxidation and one for the reduction.
- Balance each half-reaction by adding atoms and electrons to the reactants and products until the number of atoms of each element and the number of electrons are equal on both sides of the half-reaction.
- Add the two half-reactions together to get the balanced equation.
Examples of Balancing Equations, Balance the given equations by inserting the appropriate coefficients
| Unbalanced Equation | Balanced Equation | Oxidation-Reduction Method | Half-Reaction Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fe + HCl → FeCl2 + H2 | Fe + 2HCl → FeCl2 + H2 | Fe → Fe2+ + 2e–2H+ + 2e– → H2 | Fe → Fe2+ + 2e–2H+ + 2e– → H2 |
| NaOH + H2SO4 → Na2SO4 + H2O | 2NaOH + H2SO4 → Na2SO4 + 2H2O | 2NaOH → 2Na+ + 2OH–H2SO4 + 2OH– → SO42- + 2H2O | 2NaOH → 2Na+ + 2OH–H2SO4 + 2OH– → SO42- + 2H2O |
| KMnO4 + HCl → MnCl2 + Cl2 + H2O | 2KMnO4 + 16HCl → 2MnCl2 + 5Cl2 + 8H2O | MnO4– + 8H+ + 5e– → Mn2+ + 4H2O2Cl– → Cl2 + 2e– | MnO4– + 8H+ + 5e– → Mn2+ + 4H2O2Cl– → Cl2 + 2e– |
| Fe2O3 + CO → Fe + CO2 | Fe2O3 + 3CO → 2Fe + 3CO2 | Fe2O3 + 6e– → 2Fe + 3O2-CO + O2- → CO2 + 2e– | Fe2O3 + 6e– → 2Fe + 3O2-CO + O2- → CO2 + 2e– |
| NH3 + O2 → NO + H2O | 4NH3 + 5O2 → 4NO + 6H2O | NH3 + 2O2- → NO + H2O + 2e–O2 + 4e– → 2O2- | NH3 + 2O2- → NO + H2O + 2e–O2 + 4e– → 2O2- |
FAQ
What is the significance of balancing chemical equations?
Balancing chemical equations is crucial for understanding the stoichiometry of reactions, ensuring that the number of atoms of each element on the reactants’ side matches the number of atoms of the same element on the products’ side. This allows for accurate predictions of reaction outcomes and quantitative analysis.
Can you explain the oxidation-reduction method for balancing equations?
The oxidation-reduction method involves identifying the species undergoing oxidation and reduction and balancing the electrons transferred between them. This method is particularly useful for redox reactions, where electron transfer is a key aspect.
What is the role of coefficients in balancing equations?
Coefficients are numerical factors placed in front of chemical formulas to adjust the stoichiometry of a reaction. By manipulating coefficients, chemists can ensure that the number of atoms of each element is conserved throughout the reaction.