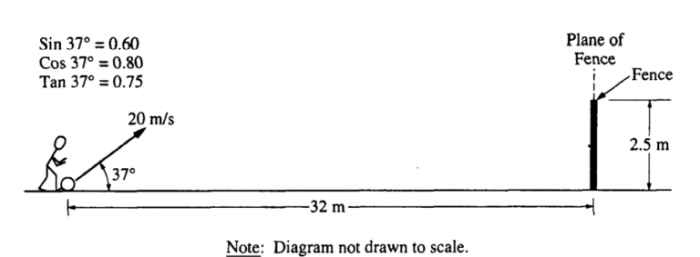
Welcome to the world of AP Physics 1 kinematics practice problems, where the study of motion takes center stage. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the fundamental principles of kinematics, providing you with a solid foundation to tackle any motion-related challenge.
From the basics of displacement, velocity, and acceleration to real-world applications in engineering and sports, we’ll explore the fascinating world of kinematics. Get ready to sharpen your problem-solving skills and gain a deeper understanding of the motion that surrounds us.
Kinematics Practice Problems: Ap Physics 1 Kinematics Practice Problems
Kinematics is the branch of physics that deals with the motion of objects. It is a fundamental topic in physics, and it has applications in many fields, such as engineering, physics, and sports.
This article provides a brief overview of the basic concepts of kinematics, as well as some practice problems to help you test your understanding. We will also discuss some of the applications of kinematics in real-world situations.
Basic Concepts
The basic concepts of kinematics are displacement, velocity, and acceleration. Displacement is the change in position of an object. Velocity is the rate of change of displacement. Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity.
These three concepts are related by the following equations:
v = u + ats = ut + 1/2 at^2v^2 = u^2 + 2as
where:
- v is the final velocity
- u is the initial velocity
- a is the acceleration
- t is the time
- s is the displacement
Problem-Solving Techniques, Ap physics 1 kinematics practice problems
When solving kinematics problems, it is important to first identify the given information and the unknown variables. Once you have done this, you can use the appropriate equations to solve for the unknown variables.
Here are some tips for solving kinematics problems:
- Draw a diagram of the situation.
- Identify the given information and the unknown variables.
- Choose the appropriate equations to use.
- Solve for the unknown variables.
- Check your answer to make sure it makes sense.
Practice Problems
Here are some practice problems to help you test your understanding of kinematics:
| Problem | Solution |
|---|---|
| A car starts from rest and accelerates at a constant rate of 2 m/s^2. How far will the car travel in 10 seconds? | 100 meters |
| A ball is thrown vertically upward with a velocity of 10 m/s. How high will the ball go? | 10 meters |
| A car is traveling at a constant speed of 30 m/s. How long will it take the car to travel 100 meters? | 3.3 seconds |
Applications in Real-World Situations
Kinematics is used in many fields, such as engineering, physics, and sports. Here are some examples of how kinematics is used in real-world situations:
- Engineers use kinematics to design bridges, buildings, and other structures.
- Physicists use kinematics to study the motion of objects in space.
- Sports scientists use kinematics to analyze the motion of athletes.
Advanced Topics
In addition to the basic concepts of kinematics, there are also some more advanced topics that you can study. These topics include:
- Relative motion
- Projectile motion with air resistance
- Circular motion
These topics are more challenging than the basic concepts of kinematics, but they are also very important in many fields.
Popular Questions
What are the key concepts covered in AP Physics 1 kinematics?
AP Physics 1 kinematics focuses on the fundamental concepts of motion, including displacement, velocity, acceleration, and the different types of motion, such as linear, circular, and projectile motion.
How can I improve my problem-solving skills in kinematics?
Practice is key! Engage in solving a variety of kinematics problems, starting with simpler ones and gradually increasing the complexity. Identify the given information, unknown variables, and appropriate equations to use.
What are some real-world applications of kinematics?
Kinematics finds applications in fields such as engineering, where it’s used to analyze the motion of machines and structures; physics, where it’s essential for understanding the behavior of objects in motion; and sports, where it helps optimize performance by analyzing athlete movements.